

Health professionals are expected to have the skills to assess and manage patients with suicidal thoughts. Project Synergy is a 3-year programme for the transformation of mental health services through the use of innovative technologies. InnoWell has been formed by the University of Sydney and PricewaterhouseCoopers to administer the $30 M Australian Government Funded Project Synergy. He is the Chief Scientific Advisor to, and an equity shareholder in, InnoWell. He was a member of the Medical Advisory Panel for Medibank Private until October 2017. He is a Board Member of Psychosis Australia Trust and a member of Veterans Mental Health Clinical Reference group. has previously led community-based and pharmaceutical industry-supported (Wyeth, Eli Lily, Servier, Pfizer, AstraZeneca) projects focused on the identification and better management of anxiety and depression. The BMC operates an early-intervention youth services at Camperdown under contract to Headspace. He is the Co-Director, Health and Policy at the Brain and Mind Centre (BMC) University of Sydney. has been a Commissioner in Australia's National Mental Health Commission since 2012. have provided expert evidence in civil, criminal and coronial matters. 96%) than studies conducted in non-psychiatric settings. 22%) and lower pooled specificity (81% v. Studies of suicidal ideation expressed by current and former psychiatric patients had a significantly higher pooled sensitivity (46% v. The pooled sensitivity of suicidal ideation for later suicide was 41% (95% CI 35–48) and the pooled specificity was 86% (95% CI 76–92), with high between-study heterogeneity. Studies conducted in primary care and other non-psychiatric settings had similar pooled odds to studies of current and former psychiatric patients (OR = 3.86 v. Further trials are necessary to evaluate the efficacy and tolerability versus other medications.There was a moderately strong but highly heterogeneous association between suicidal ideation and later suicide ( n = 71, OR = 3.41, 95% CI 2.59–4.49, 95% prediction interval 0.42–28.1, I 2 = 89.4, Q-value = 661, d.f.( Q) = 70, P ≤0.001). Our results suggest that aripiprazole is effective and safe in treating bipolar mania. Aripiprazole was also associated with higher levels of high density lipoprotein, lower dropout rates, but no difference in extrapyramidal symptoms in the maintenance phase versus a placebo or in comparison with other medications (haloperidol or lithium). Aripiprazole was associated with lower relapse rates in bipolar mania when used in combination versus a placebo in maintenance therapy (odds ratio: 0.522, p < 0.029). −0.299, p=0.001) and psychosis (Hedges' g: −0.296, p < 0.001) in the acute mania state, but did not improve depressive symptoms (Hedges' g: −0.127, p =0.054) in the acute depressive state. Compared to a placebo, aripiprazole improved acute mania (Hedges' g: A total of 20 RCTs met the eligibility criteria, including two which investigated the efficacy of aripiprazole versus haloperidol (aripiprazole =340 haloperidol =337), three which compared aripiprazole versus lithium (aripiprazole =208 lithium =212), and 15 with multiple comparisons of aripiprazole versus a placebo (aripiprazole =1923 placebo =1499). Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of people with BD who received aripiprazole were included.
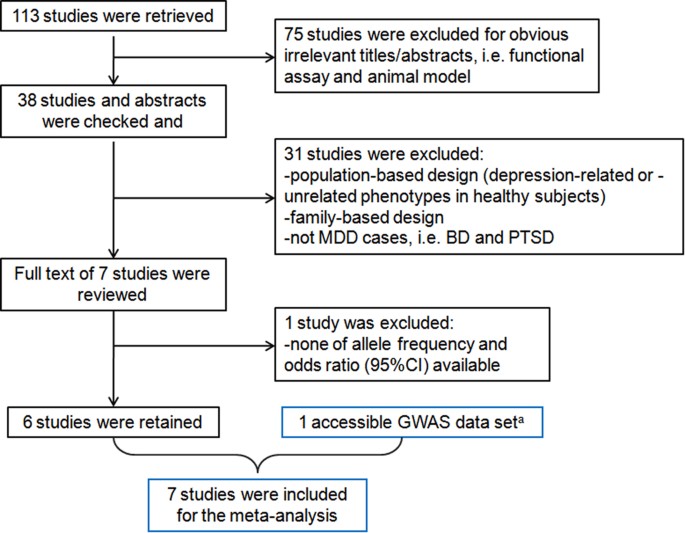
Two authors conducted systematic searches of PubMed and ScienceDirect from inception until May 14th, 2017. therefore we conducted this comprehensive meta-analysis to investigate the efficacy and safety profile of aripiprazole in treating BD.

Numerous studies have investigated aripiprazole as a treatment for bipolar disorder (BD). Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, v. Efficacy, safety and tolerability of aripiprazole in bipolar disorder : an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Progress in Neuropsychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry Please use this identifier to cite or link to this item:Įfficacy, safety and tolerability of aripiprazole in bipolar disorder : an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
